作者:Zhangjiajie World Geopark 来源:本站 浏览次数:60次
karst landform, also known as karst landform, is the general name of surface and underground forms formed by dissolved water on soluble rocks. In addition to the dissolution, it also includes the erosion of running water, submergence erosion, and other mechanical erosion processes such as collapse. The word Karst comes from the name of carbonate plateau in Istria Peninsula, northwest of the former Yugoslavia, which is locally known as a place where rocks are exposed, and "karst landform" is named as the place where modern karst research started.
There are three types of soluble rocks: 1. Carbonate rocks (limestone, dolomite, marl, etc.). 2. Sulfate rocks (gypsum, anhydrite and glauberite). 3. Halogen rocks (potassium, sodium, magnesium salt rocks, etc.), accounting for 10% of the total area of the earth. Karst landforms are developed from the tropics to the cold zone, from the mainland to the islands. Karst landforms in China are widely distributed and have a large area, mainly in the areas where carbonate rocks are exposed, covering an area of about 910,000 ~ 1.3 million square kilometers. Among them, Guangxi, Guizhou, Yunnan and the eastern part of Sichuan and Qinghai (i.e. Yunnan-guizhou Plateau) occupy the largest area, which is one of the largest karst regions in the world. It is also found in Tibet and some northern regions.
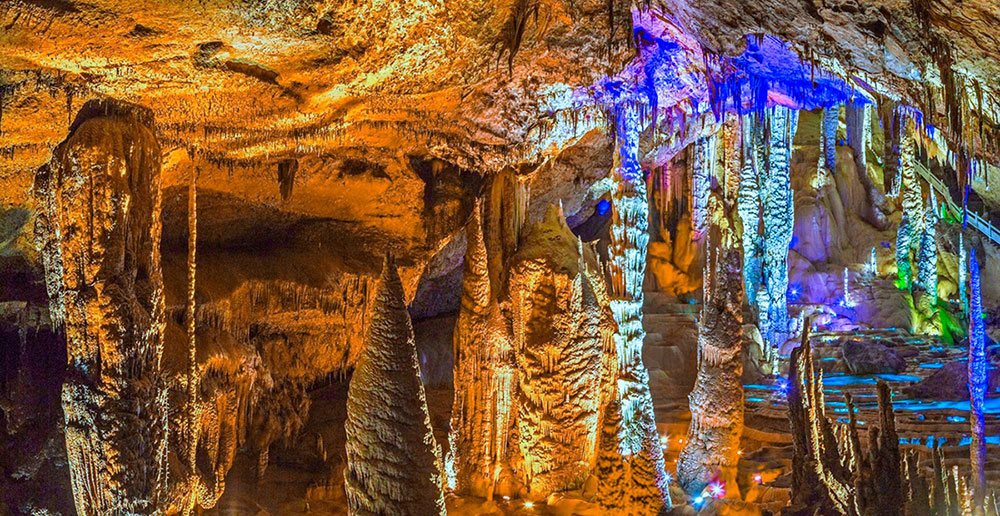

Karst cave is the underground cave formed by the expansion of groundwater along the cracks of soluble rock. The size is different, and the large one can hold more than 1000 people. The shape is strange, and there are many strange landscapes in the cave, such as stalagmites, stone columns, stalactites, stone curtains and so on. It's too small for one person to pass. The cave is the long-term result of water dissolution, water erosion and gravity. The accumulation of gravity water is the main form of karst cave accumulation landform. Water droplets dissolving a large number of soluble rocks fall intermittenously from the top of the karst cave and accumulate continuously, thus forming colorful stalactites, stalagmites, stone columns, stone curtains, and side stone embankments.

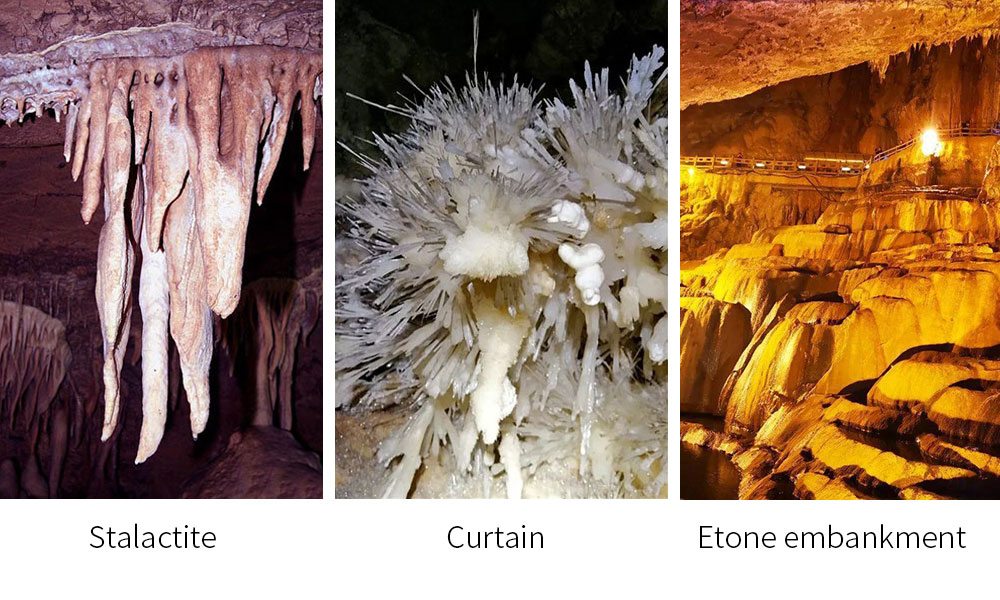
Stalactite is a kind of inverted cone-shaped karst deposits, the largest up to several meters, the small only a few centimeters, mainly karst water along the top of the cave seepage and precipitation in the drip. It's attached to the roof of the cave, and it extends down to the bottom.
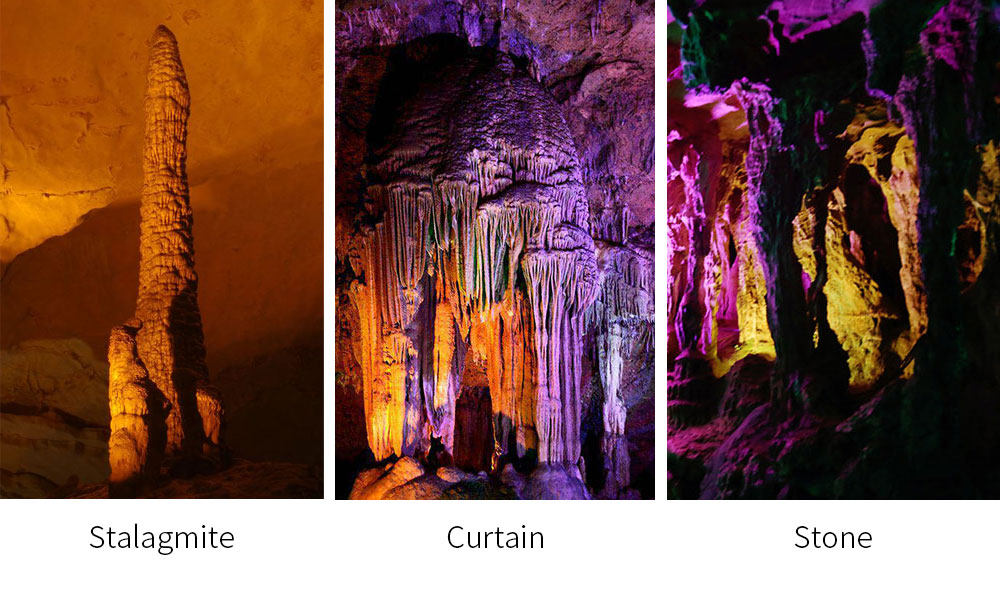
Stalagmite is a karst accumulation extending upward from the bottom of the cave, mainly the product of karst water droplets falling to the bottom of the cave and constantly deposited, it grows relative to stalactite, generally in the shape of bamboo shoots, towers and cones. Stalactites and stalagmites have concentric structure in cross section. Stalactites and stalagmites grow relatively, and gradually combine into one, with the continuous deposition of karst water, slowly form a strong stone column.
Stone mantle is the product of CaCO3 gradually deposited during the film-like flow of karst water along the cave wall. It is generally sheet-like, lamellar, and has curved streamlines, with a height of tens of meters, which is very spectacular. The edge stone embankment refers to the levee deposits on both sides of the bottom of the cave, the height is generally a few centimeters to tens of centimeters, and it is in the shape of a curved ladder. In addition, there are many strange landscapes in the cave, some like lotus blossoms, some like branches stretching, and some stone grapes, stone coral and so on.
Stalagmites are close partners of stalactites. When water droplets fall from the roof of the cave, limestone deposits are deposited on the ground. In this way, the stalagmite grows upward against the stalactite. It can be said that stalactites are "Sir" and stalagmites are "postnatal". However, the stalagmite chassis is large, itself is relatively stable, and it is not easy to break, so its "growth" rate is often faster than the stalactite. The maximum height of stalagmites can reach 30 meters, like a "stone tower" that grows out of the flat.
The stalactites that grow down will sometimes be connected with the stalagmites that grow up to form a stone column, thick at both ends and thin in the middle, and people who do not know the details also think who chiseled it out. In many limestone caves, stalactites and stalagmites are mostly not joined together; That's because the stalactite breaks off, or too much limestone blocks the droplet's path, forcing the droplet to change its path and move to another place, where a new stalactite grows. In this way, the stalactites and stalagmites will not "meet".
申明:本站文章如有侵犯您的权益,请随时联系我们删除。